Context
What is Disability?
Persons with disabilities include those who have long-term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairments which in interaction with various barriers may hinder their full and effective participation in society on an equal basis with others
UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD) Article 1
Disability and Financial Inclusion
The UNCRPD requires States Parties to take measures to ensure persons with disabilities have “…equal rights to control their own financial affairs and to have equal access to bank loans, mortgages and other forms of financial credit.” (Articles 12-15)
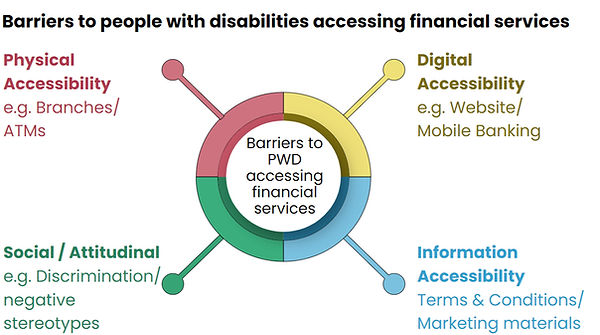
However, access to financial services remains restricted by multiple barriers including lack of accessibility of physical and digital infrastructure, information unavailable in accessible formats, and social barriers including discriminatory stereotypes of people with disabilities.
SDGs and Disability Inclusion

The commitment to ‘’leave no-one behind’’ is the central promise of the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (UNSDG). This represents a commitment to eradicate all forms of poverty, and combat discrimination and inequalities that result in individuals and groups being marginalised and excluded.
Disability is addressed across the SDGs, both directly through explicit references to "disability" and indirectly when referring to "vulnerable" and "disadvantaged groups”
The UN Capital Development Fund (UNCDF) identifies access to financial services as an enabler or target for eight of the SDGs.





Our approach to financial and economic empowerment of PWD directly addresses 4 SDGs
As women with disabilities experience particular disadvantage, there is also strong impact for gender equality